Written by
Misun
on
on
[Java/백준]9184번: 신나는 함수 실행
알아야 할 개념
메모이제이션(memoization)
동적 계획법(dynamic programming)의 핵심 기술로 동일한 계산을 반복해야 할 때, 이전에 계산한 값들을 메모리에 저장함으로써 동일한 계산의 반복 수행을 제거하여 프로그램 실행 속도를 빠르게 하는 방법이다. 보통 예시로 피보나치 수열을 사용한다.
출처 https://kimdohyeon.tistory.com/43
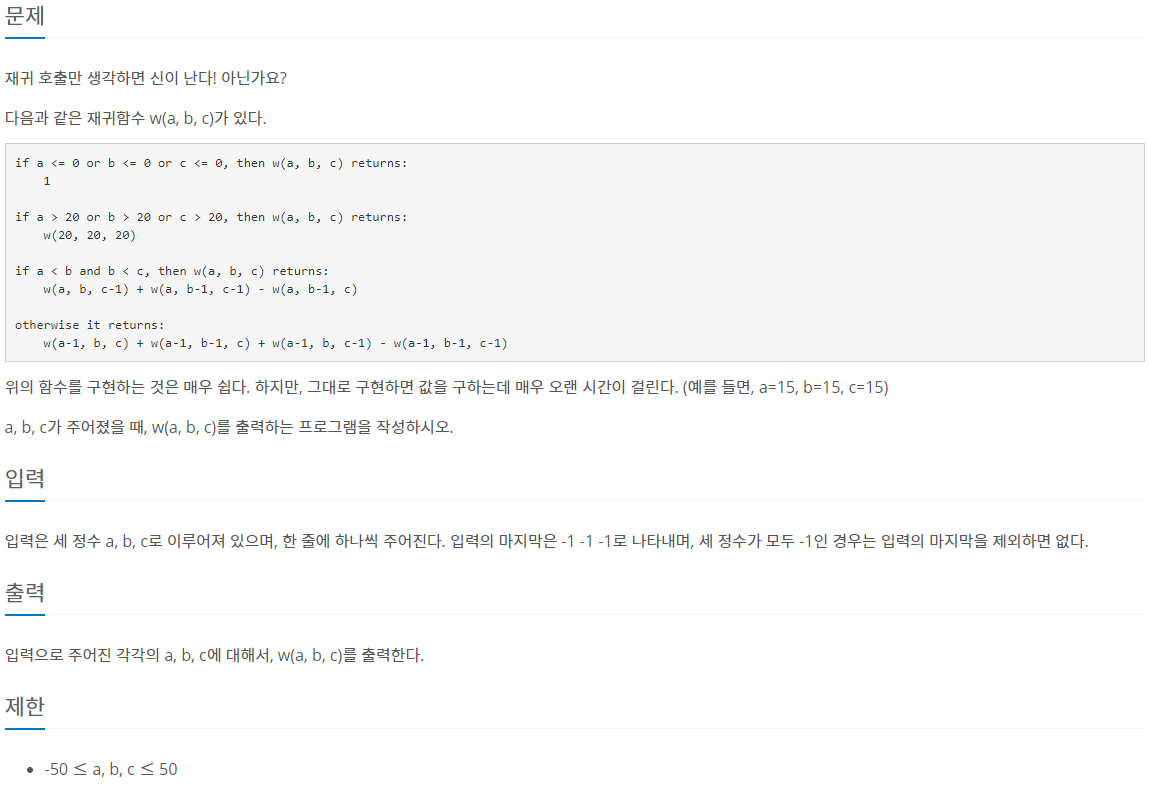
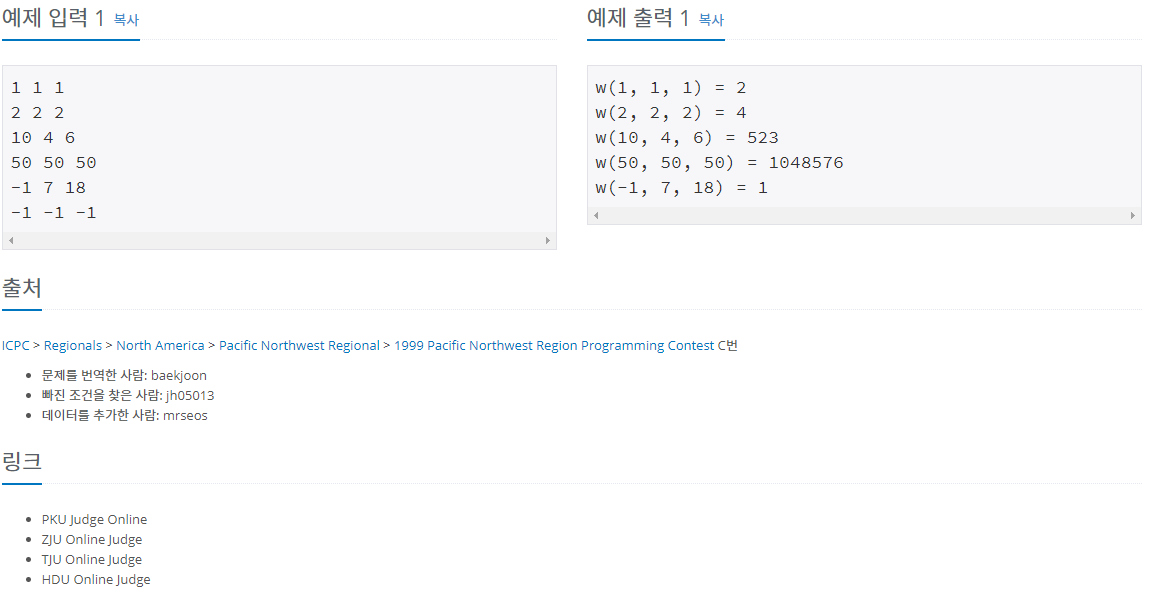
문제풀이
첫번째 방법: 시간초과 실패
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main_9184 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
boolean flag = true;
while(flag) {
String str = br.readLine();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(str, " ");
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int b = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(a==-1 && b==-1 && c==-1) {
flag = false;
break;
}
int answer = func(a,b,c);
System.out.println("w("+a+", "+b+", "+c+") = " + answer);
}
br.close();
}
static int func(int a, int b, int c) {
if(a<=0 || b<=0 || c<=0) {
return 1;
}else if(a>20 || b>20 || c>20) {
return func(20,20,20);
}else if(a<b && b<c) {
return func(a,b,c-1) + func(a,b-1,c-1) - func(a,b-1,c);
}else {
return func(a-1,b,c) + func(a-1,b-1,c) + func(a-1,b,c-1) - func(a-1,b-1,c-1);
}
}
}
시간초과로 실패했다. 시간복잡도를 파악하는 능력을 길러야하는데 아직은 푸는데 급급해서 신경을 못쓰고있다.
두번째 방법: Scanner와 메모이제이션 사용
import java.util.Scanner;
class Main_9184 {
static int memo[][][] = new int[21][21][21];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
// 모든 입력값이 -1이면 while문을 빠져나온다.
if (a == -1 && b == -1 && c == -1) {
break;
}
System.out.printf("w(%d, %d, %d) = %d\n", a, b, c, w(a, b, c));
}
}
static int w(int a, int b, int c) {
// a, b, c가 범위를 벗어나지 않으면서 메모이제이션이 되어있는 경우
if(range(a, b, c) && memo[a][b][c] != 0) {
return memo[a][b][c];
}
if (a <= 0 || b <= 0 || c <= 0) {
return 1;
} else if (a > 20 || b > 20 || c > 20) {
return memo[20][20][20] = w(20,20,20);
} else if (a < b && b < c) {
return memo[a][b][c] = w(a, b, c-1) + w(a, b-1, c-1) - w(a, b-1, c);
} else {
return memo[a][b][c] = w(a-1, b, c) + w(a-1, b-1, c) + w(a-1, b, c-1) - w(a-1, b-1, c-1);
}
}
static boolean range(int a, int b, int c) {
return 0 <= a && a <= 20 && 0 <= b && b <= 20 && 0 <= c && c <= 20;
}
}
다르게 푼 사람들 보니까 기존의 피보나치 함수를 이용하지 않고,
f(n) = (f(n-1)의 f(0)개수와 f(1)개수의 합) * f(1) + (f(n-1)의 f(1)의 개수) * f(0) 이라는 점화식을 도출하여 문제를 푸셨다.
Discussion and feedback